- April 6, 2020
- Posted by: Syed Shujaat
- Category: Cisco
No Comments
A fiber optic cable consists of one or more strands of glass, each only slightly thicker than a human hair.
There are 2 Types
- Single Mode: Thinner but Glass Core, Long Distance, More expensive and more Bandwith. It’s normally 9/125 Microns
- Multi-Mode: (Either Aqua or Orange color)Thicker but Plastic Core, Shorter Distance, Cheaper with lower Bandwidth. It’s normally 50/125 Microns
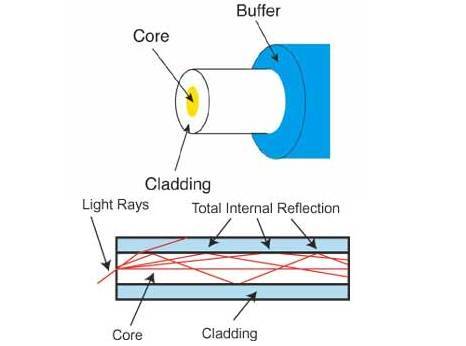
Each Fiber cables have 3 elements of which is consists of :
It’s Calculated in Microns: Millionth of a meter and measures as Core/Cladding. i.e 50/125 of Multimode
- Core : Center of each strand. provides the pathway for light to travel
- Cladding: The core is surrounded by a layer of glass called cladding that reflects light inward to avoid loss of signals
- Jacket – Buffer. The outer layer of the cable.
Fiber Optic cable has a pair of connectors on each end. Each of these is to Send/Recieve on each end.
Generally, you will use SFP connectors on Switch or routers to connect Fibers. Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) is a compact as shown below, hot-pluggable network interface module used for both telecommunication and data communications applications.

- You can also make Pre-made DAC Cable (Direct Attach Copper) SFP which is connected with Filber cable along with SFP cables.
Given Below are the Types of Fiber optics connectors.